Biomedicines, Free Full-Text
4.7 (688) · € 5.99 · En stock
Artemisia annua L. has long been known for its medicinal properties and isolation of ingredients whose derivatives are used for therapeutic purposes. The CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 enzymes belong to a large family of cytochrome P450 enzymes. These enzymes are involved in the metabolism of drugs and other xeonobiotics. It is known that various compounds can induce or inhibit the activity of these enzymes. The aim of this study was to investigate the nature of the inhibitory effect of Artemisia annua extract on CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 enzymes, as well as the type of inhibition, the presence of reversible or pseudo-irreversible inhibition, and the possible heme destruction. The methanolic extract of Artemisia annua showed an inhibitory effect on CYP2B6 (by almost 90%) and CYP3A4 enzymes (by almost 70%). A significant decrease in heme concentration by 46.8% and 38.2% was observed in different assays. These results clearly indicate that the studied plant extracts significantly inhibited the activity of CYP2B6 and CYP3A4 enzymes. Moreover, they showed irreversible inhibition, which is even more important for possible interactions with drugs and dietary supplements.
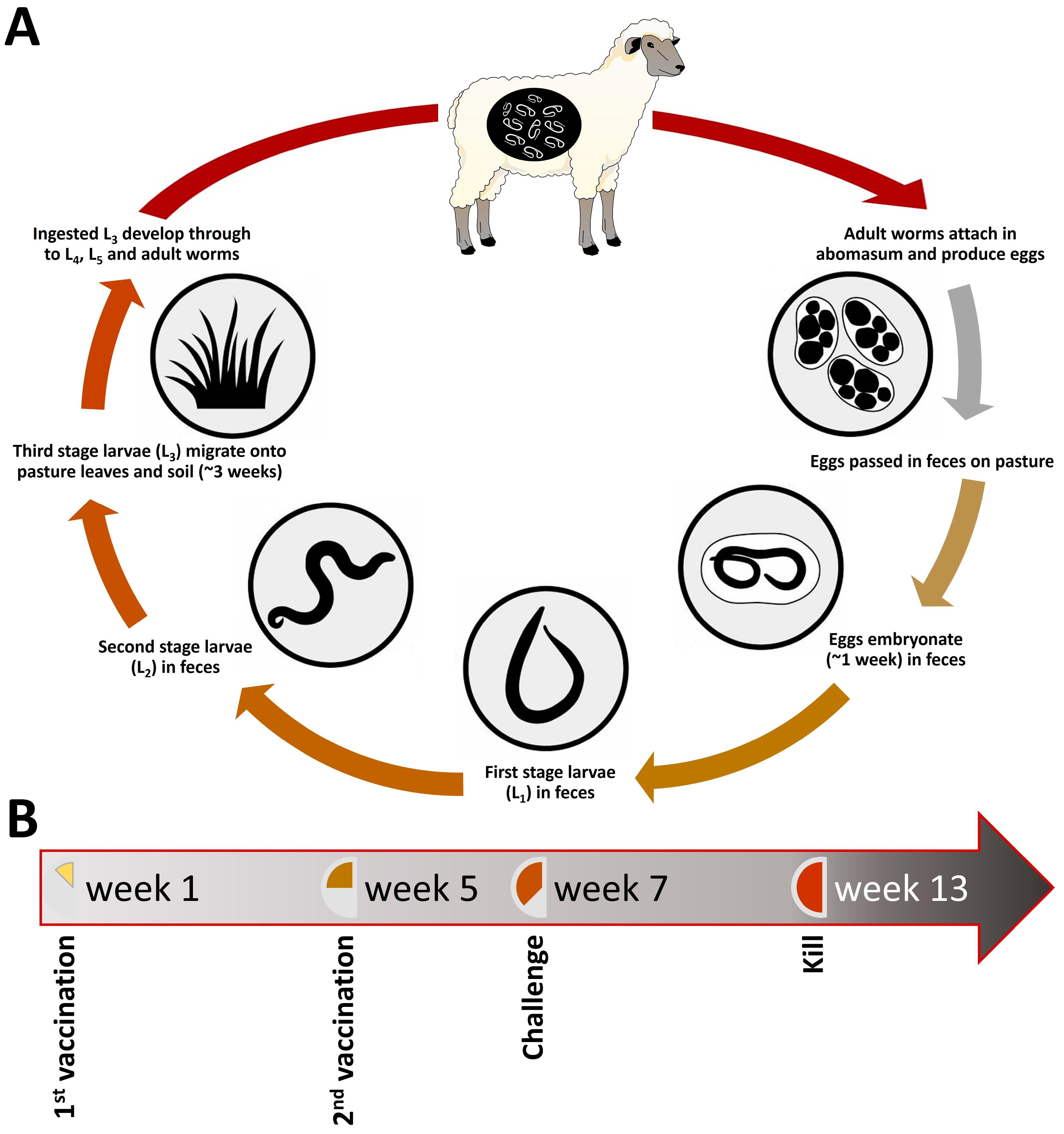
Nematodes: Science Fiction (and Scientific Fact) Under Our Feet – Seed Needs LLC, nématodes
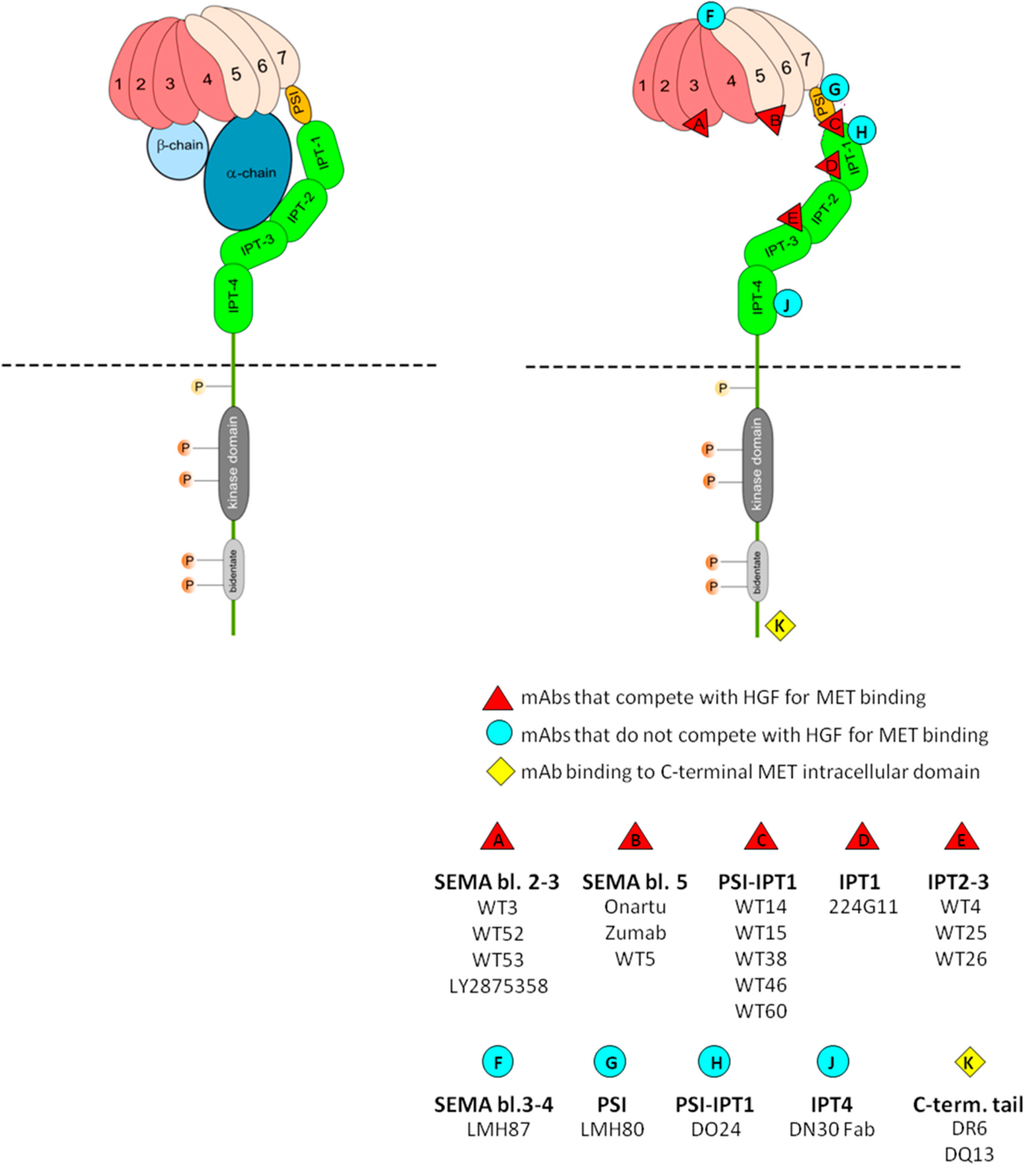
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text

Archives Biomedicine

Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, Journal

Biomedicines, Free Full-Text, Tacs
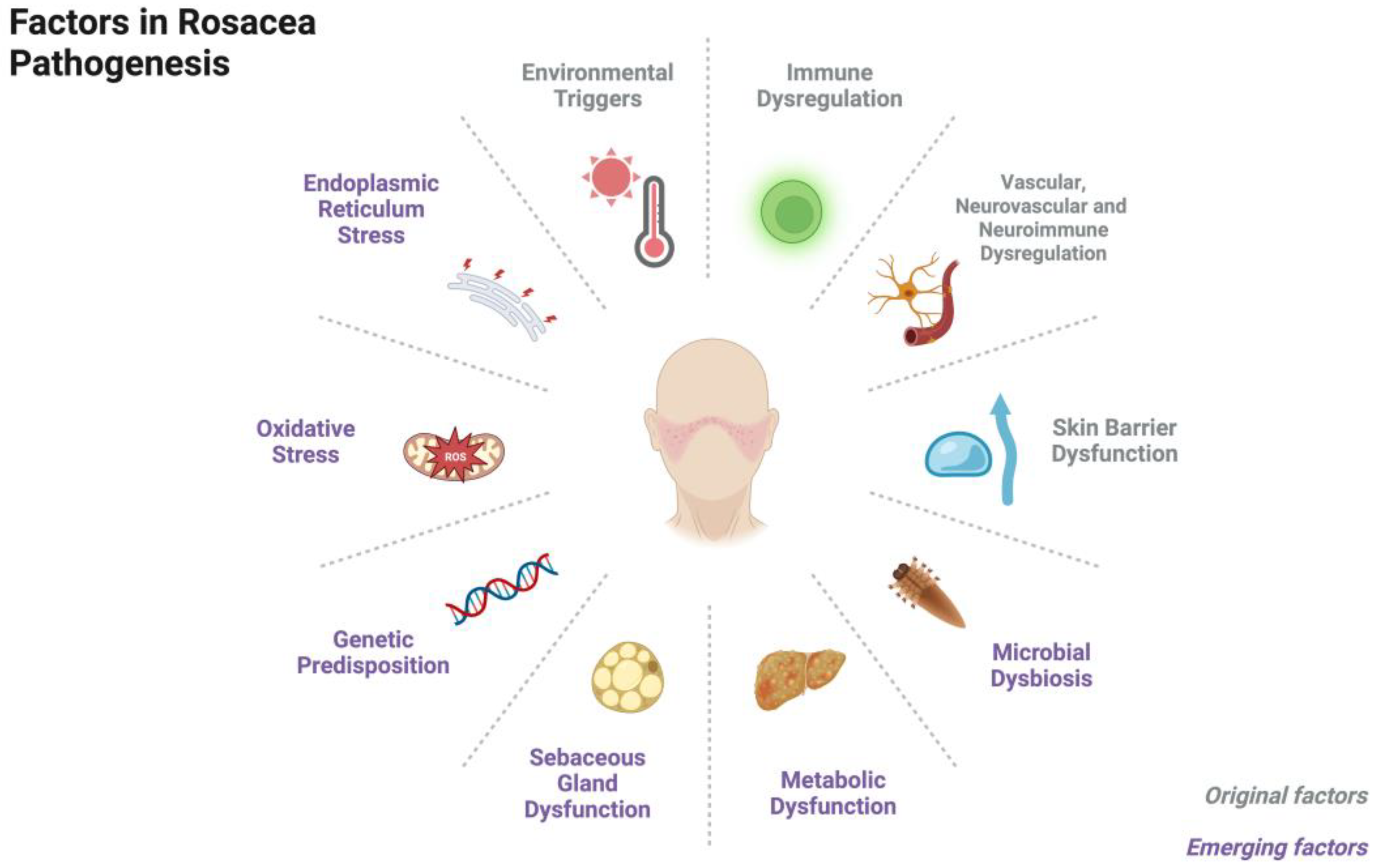
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text, retina
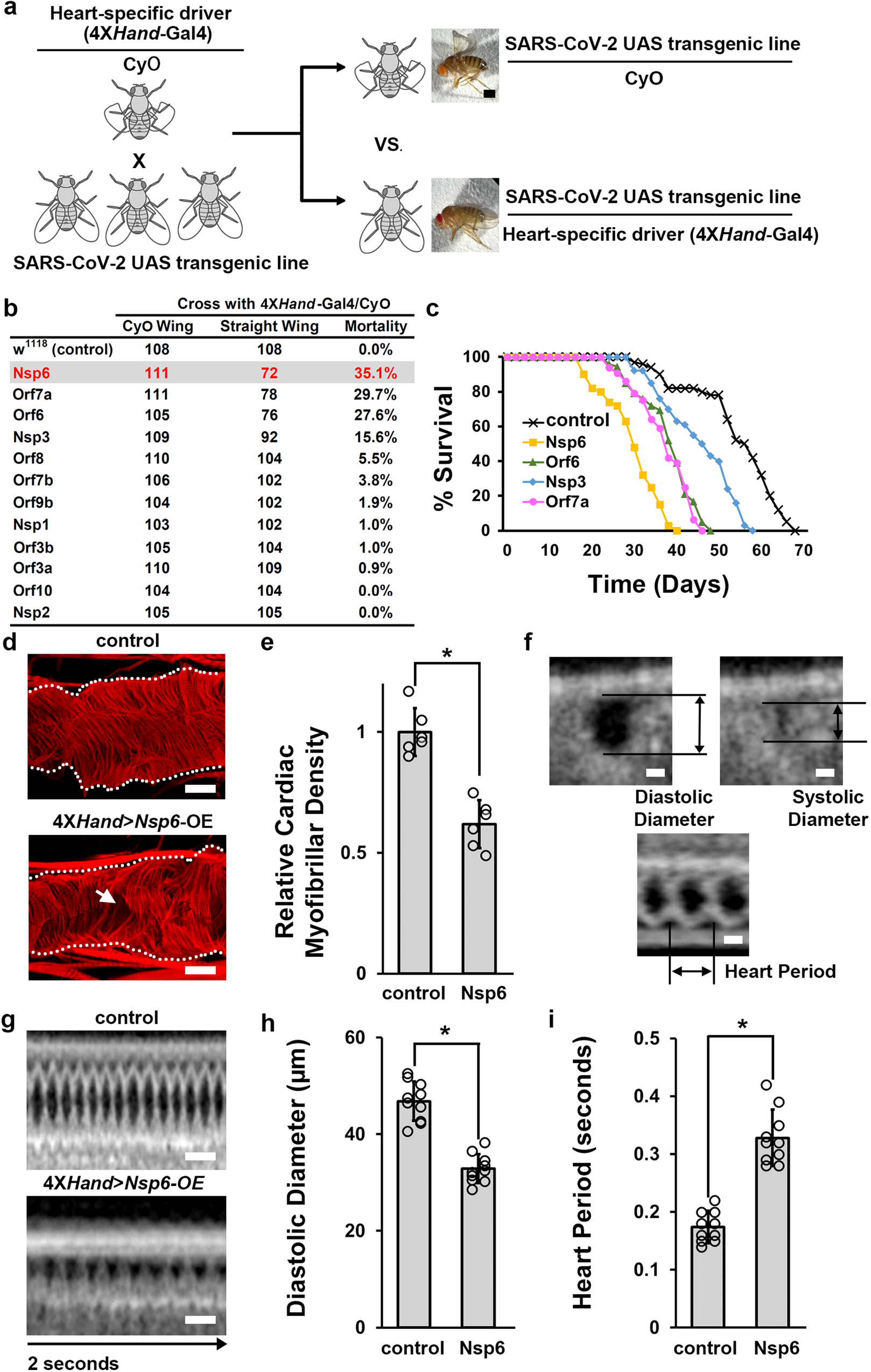
SARS-CoV-2 Nsp6 damages Drosophila heart and mouse cardiomyocytes through MGA/MAX complex-mediated increased glycolysis
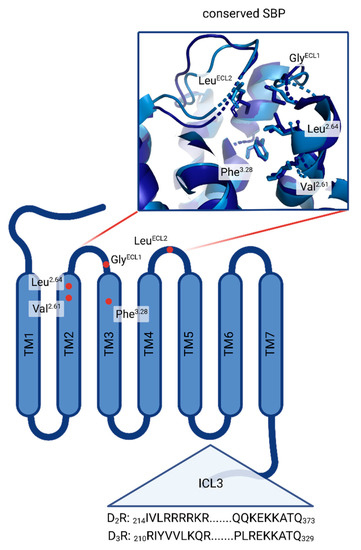
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text, retina
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text, mouse accuracy test 3d
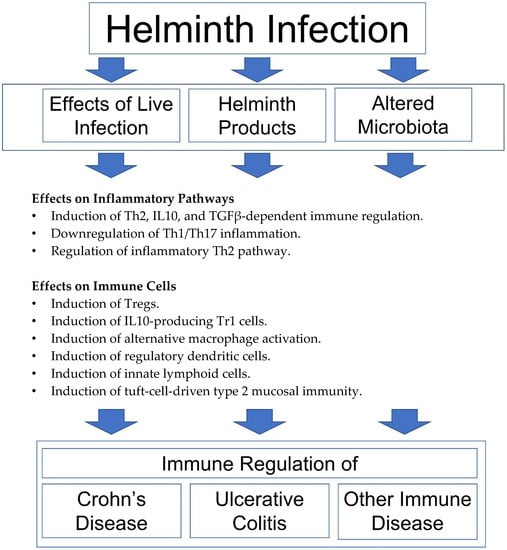
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text, gordon hayward sofascore
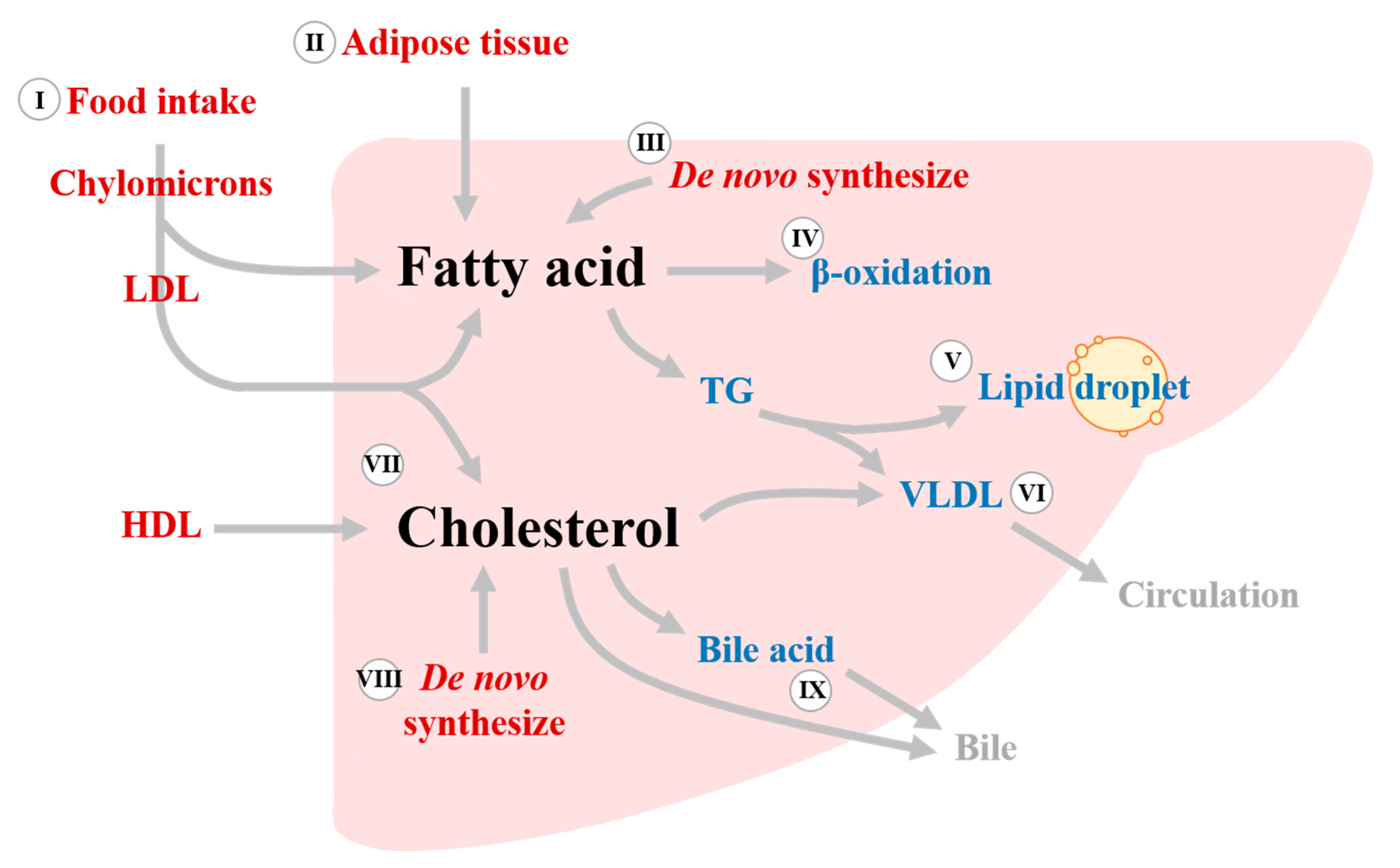
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text, Tacs

Endothelial Damage and the Microcirculation in Critical Illness - GlycoCheck
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text, kelly godoy coelho

Biomedicines, Free Full-Text, serpente google maps












