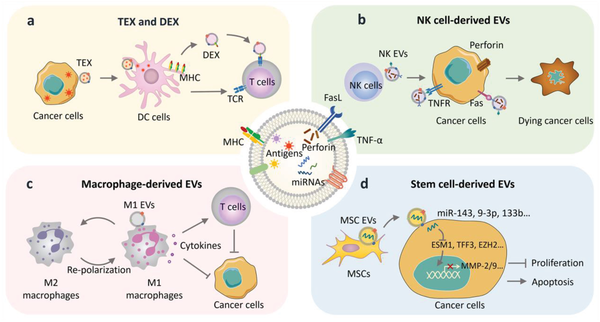
Natural EVs in cancer therapy. a) TEX stimulate immune activation by
4.9 (120) · € 14.50 · En stock
Download scientific diagram | Natural EVs in cancer therapy. a) TEX stimulate immune activation by boosting T‐cell expansion and function via APCs especially DC cells. DEX activate T cells by mimicking the role of APCs. b) NK‐cell‐derived EVs induce tumor cell death through FasL, perforin, and TNF‐α. c) EVs from M1 macrophages can re‐educate tumor associated macrophages from M2 to M1 phenotype, which further activates anti‐tumor immunity. d) Stem‐cell‐derived EVs inhibit the growth of tumor cells through miRNA‐mediated mechanisms. Abbreviations: DC cell, dendritic cell; DEX, dendritic cell‐derived EVs; FasL, Fas ligand; M1 EVs, M1 macrophage‐derived EVs; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; NK EVs, NK cell‐derived EVs; TCR, T cell receptor; TEX, tumor cell‐derived EVs; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor‐α; TNFR, tumor necrosis factor receptor. from publication: Engineered Extracellular Vesicles for Cancer Therapy | Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have emerged as a novel cell-free strategy for the treatment of many diseases including cancer. As a result of their natural properties to mediate cell-to-cell communication and their high physiochemical stability and biocompatibility, EVs are | Extracellular Vesicles, Cancer Therapy and Bioinspired | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.

Extracellular vesicle–based drug delivery in cancer immunotherapy

EXTRACELLULAR VESICLES - Engineering Extracellular Vesicles to Create Next-Generation Therapeutics

Natural EVs in cancer therapy. a) TEX stimulate immune activation by
Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) as a New Treatment for Melanoma, Journal of Skin and Stem Cell

Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Drug Resistance: Roles, Mechanisms, and Implications - Yang - 2022 - Advanced Science - Wiley Online Library

Molecules boosting plant immunity identified

Circulating extracellular vesicles are effective biomarkers for predicting response to cancer therapy - eBioMedicine

Antiviral CD8+ T-cell immune responses are impaired by cigarette smoke and in COPD

Cancer immunology - Wikipedia

Immunity, Hypoxia, and Metabolism–the Ménage à Trois of Cancer: Implications for Immunotherapy
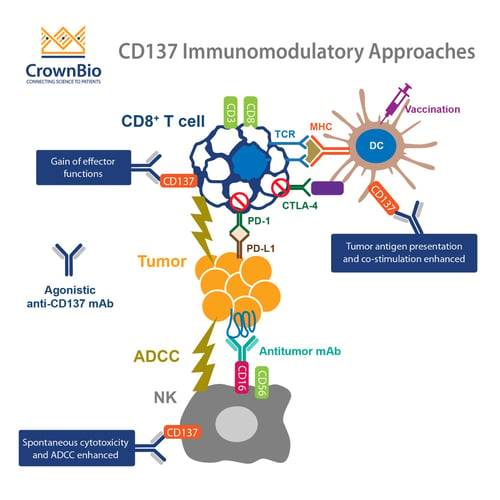
CD137: An Important Target in T Cell Co-Stimulation